This comprehensive guide throws light on the two dominant types of laptop storage – the Hard Disk Drive (HDD) and the Solid State Drive (SSD).
It delves into the intricacies of what they are, their mode of operation, strengths, weaknesses, and important factors to consider when purchasing. Further, it incorporates how to maintain these units to ensure longevity and troubleshoot common issues associated with them.
In the digital age where data is king, understanding the storage options available to us and how they work becomes imperative. Whether you’re looking to purchase a new laptop or upgrade your existing one, a significant factor to consider is the storage device it uses. A laptop’s performance, durability, and usability are significantly influenced by its storage type.
Understanding Laptop Storage
Understanding Laptop Storage
Laptop storage is the place where your computer keeps all the information it needs to function. This includes your operating system, applications, and files. The performance of your laptop heavily relies on your storage device because this is where all the data processing happens for your computer to function efficiently.
- There are two main types of storage for laptops – Hard Disk Drives (HDD) and Solid State Drives (SSD). These devices determine how quickly data can be read and written.
Hard Disk Drives (HDD)
Hard Disk Drives (HDD) use magnetism to store data on a rotating platter. A read/write head floats above the spinning platter reading and writing data.
- Because the drive has to move the head to different locations on the platter to read or write data, access times can be slower than with SSDs.
- HDDs have been the traditional form of storage for laptops due to their lower cost per gigabyte compared to SSD drives and larger capacities.
However, HDDs are more prone to failures and data loss due to their mechanical parts and are not as fast or efficient as SSDs.
Solid State Drives (SSD)
A Solid State Drive (SSD) performs the same basic function as an HDD, but data is instead stored on interconnected flash-memory chips.
- Because SSDs don’t have mechanical parts, they’re faster, quieter, and more reliable than HDDs.
- They provide quicker boot times, faster file transfers, and overall quicker computing experience.
- SSDs excel in performance, especially for tasks that access the disk drive frequently.
SSDs have higher IOPS (Input/Output Operations Per Second) which means they can read and write data much faster than HDDs. This improves the speed of applications and overall system responsiveness. See more: What is a Solid-State Drive (SSD)
The Importance of Laptop Storage
Laptop storage is crucial since it’s a core component of your computer’s operation. Without it, your computer would not ‘remember’ anything.
- It wouldn’t be able to store files, software, or even an operating system. The type of storage you choose can also influence the durability, speed, and functionality of your laptop.
Laptops with SSDs have a clear advantage in speed, durability, and power efficiency. But HDDs are still a viable option, particularly for those needing large amounts of storage space at a lower cost. In some cases, a laptop can have both, with the SSD running the operating system and applications for maximum speed, and the HDD storing large files.
Understanding the Role of Storage in Laptop Performance
Ever wondered how the type of storage impacts your laptop’s performance?
It all comes down to the speed at which your computer can read and write data.
- Solid State Drives (SSDs) are considerably quicker at performing these tasks than Hard Disk Drives (HDDs). This leads to faster program load times and quicker startup times on your laptop.
Not just speed, SSDs are also more energy-efficient than HDDs.
This is largely due to the absence of moving parts, enabling them to consume less power. As a result, laptops equipped with an SSD tend to have a longer battery life compared to those using an HDD.
Thus, comprehension of laptop storage is vital as it directly impacts the device’s performance, durability, and utility. Choosing between HDD and SSD largely relies on individual requirements. While SSDs stand out for their fast-performing and durable traits, HDDs remain a budget-friendly solution for storing copious amounts of data.
Introduction to HDD and SSD
Delving into the World of Hard Disk Drives (HDDs)
Hard Disk Drives, popularly known as HDDs, have been serving as a reliable data storage solution since the 1960s.
This technology harnesses the power of magnetism to store data on a rotating platter. A read/write head moves across this magnetic surface to store or retrieve data, depending on the operation.
Due to the mechanical elements involved, HDDs are subject to gradual wear and tear over time. They function slower and emit more noise compared to SSDs, pertaining to their mechanical nature.
The first-ever HDD, the IBM 305 RAMAC, was launched in 1956, boasting a storage capacity of 5 megabytes, a breakthrough for that period. Technological advancements since then have ensured a hike in HDD capacity, surpassing 2 terabytes today. HDDs, typically less expensive than SSDs, provide a much larger storage capacity for a lower cost per gigabyte. Some renowned manufacturers of HDDs consist of Western Digital, Seagate, and Toshiba.
Understanding Solid State Drives (SSDs)
On the other hand, Solid State Drives, or SSDs, represent a newer generation of storage devices that rely on flash-based memory. Unlike HDDs, SSDs do not have any moving parts.
Their non-volatile memory chips store data, which makes them more stable, faster, and quieter than HDDs.
The first SSDs arrived in the market in the 1990s. Despite their late arrival, SSDs soon became popular due to their blazing-fast speeds and durability under rough handling.
However, SSDs come with a high price tag, especially for large storage capacities. They are most suitable for applications that demand speed like gaming, 3D modeling, and high-definition video editing.
Leading manufacturers of SSDs include Samsung, Crucial, and Kingston. Samsung’s Evo and Pro series, in particular, are renowned for their high-speed performance and reliability.
Evolution of HDDs and SSDs
As technology advances, both types of drives continue to evolve. High-capacity magnetic drives are being developed by Seagate that use heat-assisted magnetic recording. At the same time, SSDs are continually shrinking in physical size while expanding in storage capacity.
The future of laptop storage may lie in the fusion of HDDs and SSDs, where a small SSD is used as a cache to store frequently accessed data, while an HDD holds the rest.
This hybrid provides the high speed of an SSD for commonly used data and the large storage of an HDD for other data. Brands like Western Digital and Seagate have already started producing these versions, known as SSHDs (Solid State Hybrid Drives).
Deciphering the intricacies of HDD and SSD
When it comes to HDD and SSD, the decision often hinges on various factors such as storage capacity, speed, endurance, noise, and cost. HDDs, with their vast storage space and affordable price tag, typically appeal to consumers looking for cost-effective storage solutions.
Conversely, SSDs with their speed, energy efficiency, and robustness, tend to attract those in search of performance and durability.
Ultimately, both HDDs and SSDs bring their own set of advantages and disadvantages to the table. Having a clear understanding of these is essential to making a well-informed decision on the perfect laptop storage option for your needs.

Comparing HDD and SSD
Unraveling the Nitty-Gritty of HDD vs. SSD Storage in Laptops
Hard Disk Drive (HDD) and Solid State Drive (SSD) represent two distinct types of storage systems found in laptops. Each has its own unique operating principles, cost structure, storage space, speed, and longevity. Suitable choice of storage type primarily rests on assessing and understanding their individual strengths and shortcomings.
Speed: HDD vs. SSD
When it comes to speed, SSDs outperform HDDs.
SSDs use flash memory to deliver superb performance and high-speed data transfer. On the other hand, HDDs use a mechanical arm with a read/write head to move around and read information from the right location on the storage platter.
HDDs can be slower because of the time it takes for the HDD to speed up to operating specs, which an SSD can access instantly.
Durability: HDD vs. SSD
Regarding durability, SSDs take the lead again. HDDs contain moving parts – the platters, the read/write arm, and the spinning motor.
These parts can get damaged, especially when the laptop is jolted or dropped while in operation. On the flip side, SSDs have no moving parts, making them more robust and less susceptible to physical shock.
Capacity: HDD vs. SSD
Contrarily, when considering storage capacity, HDDs generally offer more space for less money. You could potentially purchase a 2TB hard drive for less than a 1TB SSD.
Therefore, if you require a large amount of storage without breaking the bank, an HDD might be the better option.
Cost: HDD vs. SSD
Cost is another crucial factor to consider when choosing between HDD and SSD. HDDs are notably cheaper and offer more storage for less money.
On the other hand, SSDs, while more expensive, offer faster performance, are more durable, and consume less energy.
Energy Efficiency: HDD vs. SSD
SSDs are more energy-efficient compared to their HDD counterparts. They don’t have to power any moving parts like HDDs, which require more power to spin their magnetic platters.
Reduced energy use can lead to longer battery life in laptops, making SSDs a more suitable choice for users who require portability.
Deciding between an HDD and SSD for laptop storage requires a careful evaluation of individual needs.
If your priorities lean towards fast performance, superior durability, and high energy efficiency, an SSD is certainly an option to contemplate.
Conversely, if your decision is more budget-centric and accompanied by the need for ample storage space, choosing an HDD would be a more appropriate selection.

Buying guide for SSDs and HDDs
HDD vs. SSD – Evaluating Storage Capacity
One of the crucial aspects to weigh when buying a laptop with either an SSD or HDD storage is the capacity it offers.
HDDs, given their longer existence, have seen more development and thus provide larger storage capacities at a typically lower cost per gigabyte. Present-day HDDs can usually be found varying from 500GB to 2TB.
On the other hand, although SSDs may cost more per gigabyte, the price difference is gradually narrowing.
SSDs are usually available within the range of 120GB to 1TB. Nevertheless, for those in need of extra storage, external storage devices are always a viable alternative.
See more: ADATA Legend 850L SSD In-Depth: A Powerhouse of Speed and Compatibility
Speed and Laptop Performance
The speed of SSDs and HDDs can greatly affect your machine’s performance.
An SSD-equipped PC will boot in seconds, and apps and games can load up quickly. This has to do with the fact that SSDs don’t have mechanical parts and thus can access data much quicker.
HDDs, on the other hand, have mechanical parts and are slower. Boot time, as well as app and game load times, are noticeably slower on an HDD. However, this only generally affects load times. Once an app or game is loaded, the difference isn’t as noticeable.
Interested in gaming? read: Pick The Perfect SSD For Gaming Success
Price to Performance Ratio
When considering the price-to-performance ratio, HDDs offer a good value for money. They can store a lot of data at a low price.
SSDs, however, are more expensive, but they offer faster speeds and better performance. If you want a balance between cost and performance, consider a laptop with both an SSD for the operating system and applications, and an HDD for storing larger files.
Reliability and Data Safety
SSDs are more reliable than HDDs due to a lack of moving parts. They are resistant to shock and vibration, making them more durable.
They are less likely to fail mechanically, making them safer for your data. Meanwhile, HDDs have mechanical parts, making them sensitive to shock and vibration. This means they are more likely to fail, which can result in data loss.
Noise and Heat Production
SSDs are silent because they don’t have any moving parts. They also produce very little heat, which can be beneficial for keeping your laptop cool under heavy loads.
HDDs, on the other hand, can generate noise and heat as they run. This is because they use motors to spin the disks where information is stored, which can cause noise and heat generation.
Power Usage
Lastly, power usage is also a factor to consider. SSDs use less power than HDDs since they don’t have to power any mechanical parts.
This can lead to a longer battery life for your laptop, which can be a significant benefit if you’re frequently on the move.
Choosing the Right Laptop Storage for Your Needs
When you’re in the market for a new laptop, the first thing you need to do is consider your specific needs. If you’re dealing with a significant quantity of large files or you’re hunting for the most cost-efficient option, a Hard Disk Drive (HDD) could be the right choice for you.
However, if things like speed, performance, and dependability are at the forefront of your decision, and you possess the budget to support it, a Solid State Drive (SSD) might be your better bet.
For those seeking a balance, some laptops come equipped with both an SSD for operating systems and essential apps and an HDD for general mass storage.
It’s crucial to understand that the type of storage you choose will have a significant impact on your laptop’s functionality, cost, and lifespan.

Maintenance and common issues of HDD and SSD
A Closer Look at HDD and SSD Storage
Laptops primarily employ two types of storage systems: Hard Disk Drives (HDD) and Solid State Drives (SSD).
HDDs, a long-time staple in laptop and computer technology, operate through mechanical elements – a magnetically coated metal platter is responsible for data storage.
In contrast, SSDs represent more recent, swifter, and pricier technology. SSDs utilize a network of interconnected flash-memory chips for storage, without moving parts. This difference in structure largely defines the disparities in performance and cost between HDDs and SSDs.
Proper Maintenance of HDDs and SSDs for Longevity
To ensure the longevity and optimal function of both HDDs and SSDs, regular maintenance is necessary.
This includes regular cleaning of your device to avoid excessive dust build-up, which can cause overheating and potentially decrease the lifespan of your storage devices; ensuring that your device is protected from physical shocks and impacts, which can damage HDDs more than SSDs due to their mechanical parts, and keeping your laptop at a moderate temperature.
It’s important to run regular disk checks to identify and fix potential errors.
For HDDs, these can be mechanical failings and for SSDs, these could be corrupt blocks. Most operating systems have tools that enable users to perform these checks and repairs.
It’s also beneficial to periodically defragment HDDs to maintain performance. However, SSDs do not require defragmentation and can actually be harmed by the process.
Identifying Common Issues with HDD and SSD Storage
Common issues with HDDs often involve noticeable changes in performance, such as slow load times, difficulty retrieving files, and freezing during use. HDDs can also make unusual noises if the mechanical parts fail.
For SSDs, problems can also be exhibited through slow performance. However, because there are no mechanical parts, diagnosing problems can be a bit more challenging.
SSDs have a limited life span based on the number of write cycles, meaning they can only save a certain amount of data before they fail. If your SSD is old or heavily used, it could be approaching the end of its lifespan.
Troubleshooting and Resolving Storage Device Issues
When problems arise with HDDs or SSDs, it’s important to troubleshoot and resolve these as soon as possible. Using the in-built tools in your operating system is a good starting point. Tools such as Check Disk for Windows or Disk Utility for macOS can help identify and repair errors.
For performance-related issues, it’s recommended to clear out temporary or unnecessary files, close any programs not in use, and ensure your system is up-to-date. If a hard drive seems to be failing, it’s essential to back up data immediately and consider replacing the drive.
For SSDs showing signs of nearing the end of their lifespan, the only solution is to back up your data and replace the drive. SSD technology is continually improving, and newer models provide longer lifespans than older ones.
Understanding HDDs and SSDs, properly maintaining them, and knowing how to troubleshoot and resolve issues can help ensure the longevity and performance of your laptop storage.
Whether you have an HDD or an SSD, proper care and prompt response to issues can make the difference in how well and how long your laptop storage functions.
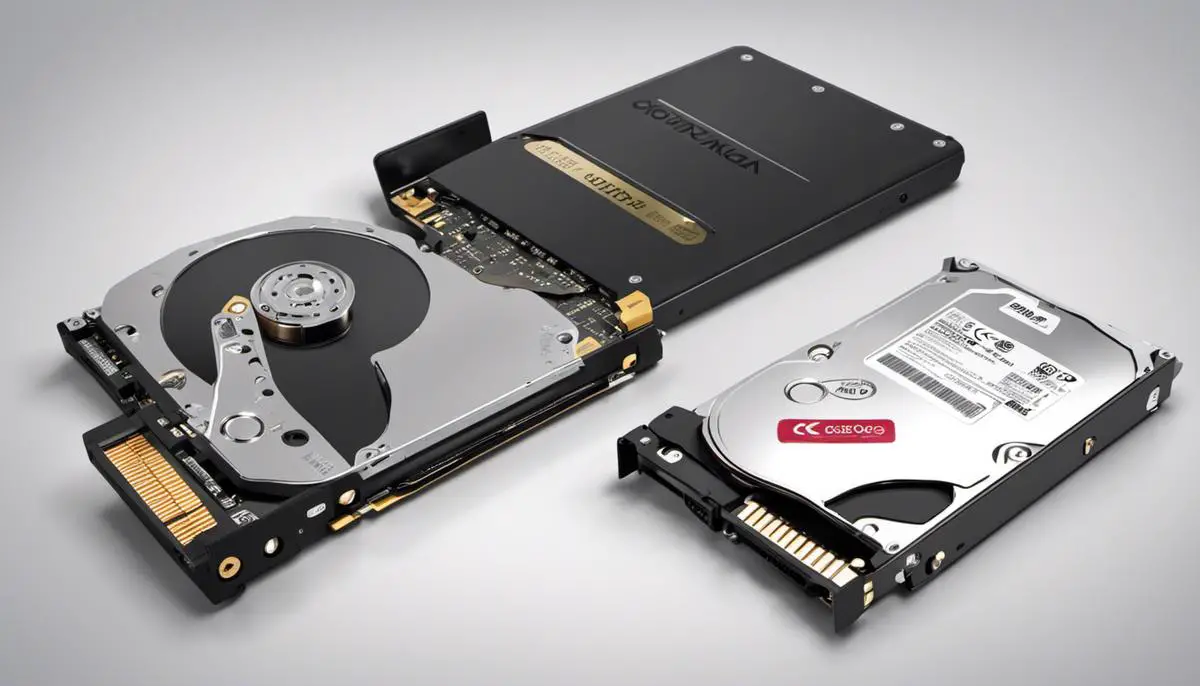

Keeping in mind the volume of tech advancements, it can be quite a task to stay informed about the diverse storage options available in the laptop market.
A sound understanding of your storage device choices —HDD and SSD— can considerably affect the performance, durability, and overall lifespan of your laptop. By taking into account their individual characteristics such as speed, durability, capacity, cost, and energy efficiency, you can make an informed decision that best aligns with your needs and preferences.
Consider the buying guide as your roadmap when navigating the purchase process. Furthermore, ensuring the regular maintenance of your storage devices and understanding the common issues that may arise can help optimize their functionality and longevity. Stay informed and equipped with this knowledge to make the most out of your laptop storage.
- Best Laptops for AI and Machine Learning
- Upgrading SSD Storage in the ThinkPad X9-15 Gen 1 Aura Edition
- How Quantum Computing Could Impact Everyday Laptops
- What Is The Difference Between Lenovo’s Pens? (with Part Numbers)
- Legion 5 Laptop Upgrade Guide: Game Like a Pro
- How to Replace Your Laptop Battery: A Step-by-Step Guide
- IdeaPad Gaming 3 Upgrade (Full Specs)
- Shut Down a Lenovo Laptop: Quick and Easy


